Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (34): 5490-5496.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.34.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cloning and expression of Asperguillus endo-chitosanase gene in Escherichia coli
Lu Hua-ding, Lian Li-yi, Chen Ming-wei, Dai Yu-hu
- Department of Orthopedics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2014-07-26Online:2014-08-20Published:2014-08-20 -
Contact:Lu Hua-ding, Department of Orthopedics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Lu Hua-ding, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Orthopedics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82172040; the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. S2011010004808 and S2013010016385; the Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province, No. 2012B031800451
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Hua-ding, Lian Li-yi, Chen Ming-wei, Dai Yu-hu. Cloning and expression of Asperguillus endo-chitosanase gene in Escherichia coli[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5490-5496.
share this article
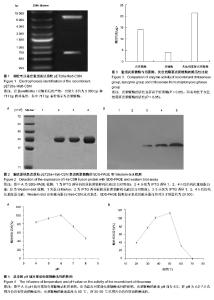
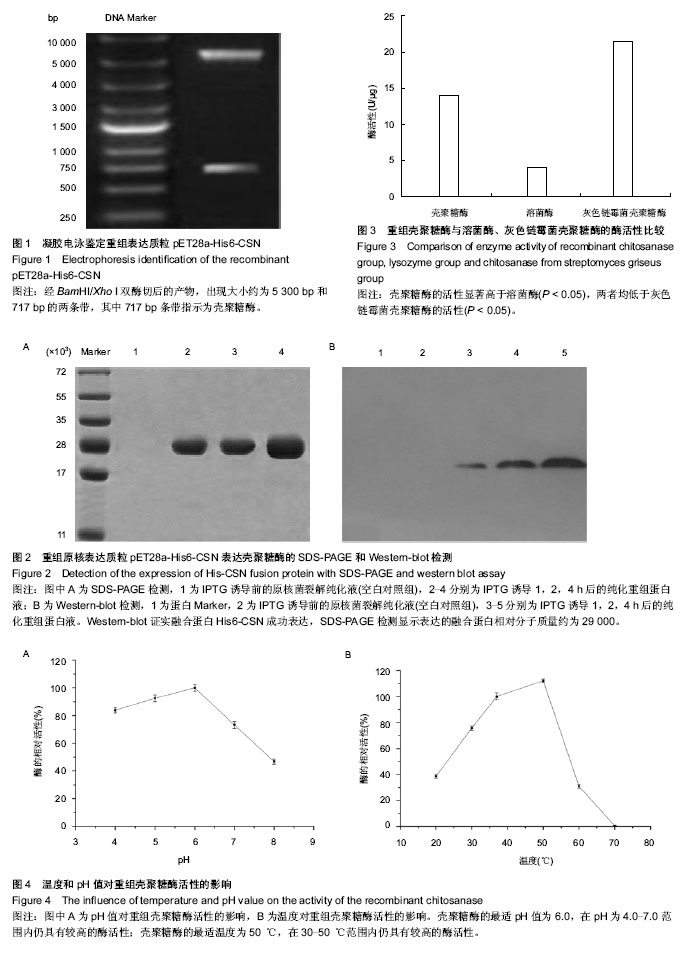
2.1 壳聚糖酶基因片段的PCR扩增 根据设计的壳聚糖酶基因序列所合成的23条引物,互为模板通过PCR拼接法扩增出目的片段,大小为717 bp,与曲霉菌CJ22-326内切型壳聚糖酶基因全长大小相符。 2.2 壳聚糖酶基因的克隆及双酶切鉴定 质粒pET-28a(+)多克隆位点的两端有限制性内切酶BamHI/Xho I的识别位点,重组表达质粒进行BamHI/Xho I双酶切,进行琼脂糖凝胶电泳鉴定,获得约为5 300 bp和717 bp两个条带(图1), 证实构建重组原核表达质粒pET28a-His6-CSN成功。 2.3 重组原核表达质粒pET28a-His6-CSN表达壳聚糖酶的SDS-PAGE和Western-blot检测 在IPTG诱导下,原核表达质粒pET28a-His6-CSN在E.coli BL21表达His6-CSN融合蛋白,使用Ni2+-NTA亲和层析得到纯化的融合蛋白。 在SDS-PAGE中,经马考斯亮蓝染色后只有一个条带在相对分子质量29 000处出现,且在诱导表达1-4 h过程中,表达的融合蛋白的量逐渐增多,对照组不表达融合蛋白(图2A)。 Western-blot检测在相对分子质量25 000与35 000之间出现一蛋白条带(图2B),该条带为纯化的融合蛋白His6-CSN。 2.4 原核表达融合蛋白His6-CSN的酶活性检测 根据所得的氨基葡萄糖NAG作标准曲线,确定壳聚糖酶水解壳聚糖所产生的还原糖的量。在37 ℃、pH=6.0条件下,壳聚糖酶的活性为(14.055±0.375) U/μg,显著高于溶菌酶的活性(4.046±0.177) U/μg,两者均低于灰色链霉菌壳聚糖酶的活性(21.442±0.463) U/μg,差异有显著性意义(F=1 773.18,P < 0.05),见图3。 2.5 pH和温度对壳聚糖酶活性的影响 壳聚糖酶的最适pH值为6.0,且酶活性在pH为4.0-7.0范围内仍具有较高的活性;当pH=7.0时仍可达最高活性的73%;当pH=8时,酶活性下降为最高活性的46%(图4A)。 壳聚糖酶的最适温度为 50 ℃,且在37 ℃时酶活性仍可达最大活性的89%;当温度为60 ℃时,酶活性急剧降低,仅为最高活性的30%;当温度为70 ℃时,酶完全失活(图4B)。"
| [1] Kasaai MR.Various methods for determination of the degree of N-acetylation of chitin and chitosan: a review.J Agric Food Chem.2009;57(5):1667-1676. [2] 张伟,林红,陈宇岳.甲壳素和壳聚糖的应用及发展前景[J].南通大学学报:自然科学版,2006,5(1):29-33. [3] 李婷,胡小喜,周幸芝,等.从虾蟹壳中提取甲壳素的研究进展[J].食品工业,2014,35(6):209-212. [4] 杨久林,谢红国,于炜婷,等.组织工程用壳聚糖研究进展[J].功能材料,2013,44(11):1521-1525. [5] Raftery R,O'Brien FJ,Cryan SA.Chitosan for gene delivery and orthopedic tissue engineering applications. Molecules. 2013;18(5):5611-5647. [6] Thirugnanasambandham K,Sivakumar V,Prakash MJ.Application of chitosan as an adsorbent to treat rice mill wastewater--mechanism, modelling and optimization. Carbohydr Polym.2013;97(2):451-457. [7] Kouzai Y,Mochizuki S,Saito A,et al.Expression of a bacterial chitosanase in rice plants improves disease resistance to the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant Cell Rep. 2012;31(4):629-636. [8] 单晓雪,郑人源,张涛,等.壳聚糖酶的研究进展[J].成都医学院学报,2007,2(3): 192-198. [9] Jaiswal M,Chauhan D,Sankararamakrishnan N.Copper chitosan nanocomposite: synthesis, characterization, and application in removal of organophosphorous pesticide from agricultural runoff.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.2012;19(6):2055-2062. [10] 李广峰,杨建东.壳聚糖纳米粒子基因载体的研究现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(47):8879-8882. [11] Dai H,Jiang X,Tan GC,et al.Chitosan-DNA nanoparticles delivered by intrabiliary infusion enhance liver-targeted gene delivery.Int J Nanomedicine.2006;1(4): 507-522 [12] Jean M,Alameh M,De Jesus D,et al.Chitosan-based therapeutic nanoparticles for combination gene therapy and gene silencing of in vitro cell lines relevant to type 2 diabetes. Eur J Pharm Sci.2012;45(1-2):138-149. [13] Plapied L,Vandermeulen G,Vroman B,et al.Bioadhesive nanoparticles of fungal chitosan for oral DNA delivery.Int J Pharm.2010;398(1-2):210-218. [14] Gao S,Chen J,Dong L,et al.Targeting delivery of oligonucleotide and plasmid DNA to hepatocyte via galactosylated chitosan vector.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2005; 60(3):327-334. [15] Smith JK,Moshref AR,Jennings JA,et al.Chitosan sponges for local synergistic infection therapy: a pilot study.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2013;471(10):3158-3164. [16] Liang DC,Liu WG,Zuo AJ,et al.Pre-deliver chitosanase to cells: a novel strategy to improve gene expression by endocellular degradation-induced vector unpacking. Int J Pharm. 2006; 314(1):63-71. [17] Jarmila V,Vavrikova E.Chitosan derivatives with antimicrobial, antitumour and antioxidant activities--a review.Curr Pharm Des.2011;17(32):3596-3607. [18] Liu YL,Jiang S,Ke ZM,et al.Recombinant expression of a chitosanase and its application in chitosan oligosaccharide production.Carbohydr Res.2009;344(6): 815-819. [19] 金春阳,赵天勤,方良,等.壳寡糖作为基因载体的体外评价[J].医药导报,2013,32(9):1115-1119. [20] Goo BG,Park JK.Characterization of an alkalophilic extracellular chitosanase from Bacillus cereus GU-02.J Biosci Bioeng.2014;117(6):684-689. [21] Sugita A,Sugii A,Sato K,et al.Cloning and characterization of a gene coding for a major extracellular chitosanase from the koji mold Aspergillus oryzae.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012;76(1):193-195. [22] Trombotto S,Ladaviere C,Delolme F,et al.Chemical preparation and structural characterization of a homogeneous series of chitin/chitosan oligomers. Biomacromolecules. 2008; 9(7):1731-1738. [23] Sinha S,Tripathi P,Chand S.A new bifunctional chitosanase enzyme from Streptomyces sp. and its application in production of antioxidant chitooligosaccharides.Appl Biochem Biotechnol.2012;167(5):1029-1039. [24] 张文清,夏玮,徐欢,等.非专一性酶催化壳聚糖水解反应的特性[J].功能高分子学报, 2003,16(1):44-48. [25] 黄惠莉,朱利平.壳聚糖酶的研究进展[J].食品工业科技, 2012, 33(6):439-443. [26] Xia W,Liu P,Liu J. Advance in chitosan hydrolysis by non-specific cellulases. Bioresour Technol. 2008;99(15): 6751-6762. [27] Li S,Chen L,Wang C,et al.Expression, purification and characterization of endo-type chitosanase of Aspergillus sp. CJ22-326 from Escherichia coli. Carbohydr Res. 2008; 343 (17): 3001-3004. [28] 涂绍勇,杨爱华,梅双喜,等. 3,5-二硝基水杨酸法(DNS)测定壳聚糖酶活力的探讨[J].食品科技,2012,37(1):240-242. [29] Chen X,Zhai C,Kang L,et al.High-level expression and characterization of a highly thermostable chitosanase from Aspergillus fumigatus in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Lett. 2012; 34(4):689-694. [30] Wang J,Zhou W,Yuan H,et al.Characterization of a novel fungal chitosanase Csn2 from Gongronella sp.JG.Carbohydr Res.2008;343(15):2583-2588. [31] Choi YJ, Kim EJ,Piao Z,et al.Purification and characterization of chitosanase from Bacillus sp. strain KCTC 0377BP and its application for the production of chitosan oligosaccharides. Appl Environ Microbiol.2004;70(8): 4522-4531. [32] 龚香艺,吴静,邬敏辰.真菌壳聚糖酶研究进展[J].食品科学, 2012, 33(17):308-311. [33] Rodriguez-Martin A,Acosta R,Liddell S,et al.Characterization of the novel antifungal chitosanase PgChP and the encoding gene from Penicillium chrysogenum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010;88(2):519-528. [34] Cheng CY,Chang CH,Wu YJ,et al. Exploration of glycosyl hydrolase family 75, a chitosanase from Aspergillus fumigatus. J Biol Chem.2006;281(6):3137-3144. [35] Heggset EB,Dybvik AI,Hoell IA,et al.Degradation of chitosans with a family 46 chitosanase from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2).Biomacromolecules.2010;11(9):2487-2497. [36] Katsumi T,Lacombe-Harvey ME,Tremblay H,et al.Role of acidic amino acid residues in chitooligosaccharide-binding to Streptomyces sp. N174 chitosanase.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2005;338(4):1839-1844. [37] 申杰,叶希韵,沈菊,等.壳寡糖对高脂血症小鼠降血脂及肝脏保护的作用[J].西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2007,35(9): 35-38. [38] 张沛,韩宝芹,陈列欢,等.用酶解法制备壳寡糖及其对机体免疫功能的调节作用[J].中国免疫学杂志,2013,29(2):191-196. [39] 金黎明,魏长征,田文杰,等.壳寡糖及其衍生物对体外培养成骨细胞增殖的作用特点[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(19):3637-3640. [40] 康立新,周玉玲,马立新.壳聚糖酶的克隆表达与壳寡糖的制备分析[J].生物技术,2012,22(2):20-23. [41] 程仕伟,孙爱友.酶法制备甲壳低聚糖研究的进展[J].生物加工过程,2011,9(5):65-70. [42] 吴爱祥.固态发酵黑曲霉产壳聚糖酶的纯化及其性质研究[J].华西药学杂志,2010,25(1):106-108. [43] 杨俐,余蓉.贵州绿僵菌产壳聚糖酶的纯化鉴定及高产菌株的诱变选育[D]. 四川大学:微生物与生化药学,2007. [44] 孙玉英,张继泉,王淑军.芽孢杆菌Bacillus sp.S-1壳聚糖酶基因的克隆与序列分析[J].中国生物工程杂志,2009,29(5):72-77. [45] 徐瑞,郭占云,戚正武.壳聚糖酶的纯化、基因克隆、及其酶学特性的鉴定[J].药物生物技术,2008,15(2):94-99. [46] 孙玉英,张继泉,王淑军,等.酶促反应制备壳寡糖条件的研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2008,28(11):67-71. [47] 杨俐,张涛,李晓红,等.固态发酵贵州绿僵菌产壳聚糖酶的亲和层析纯化及其性质研究[J].四川大学学报:医学版,2007,38(4): 713-716. [48] 方文建,隋斯光,郑连英.青霉菌产壳聚糖酶制备低分子量壳聚糖的研究[J].中国医药工业杂志,2006,37(2):85-88. |
| [1] | Wang Chun-hong, Li Zhe, Wang Ming-han, Deng Li-li, Wang Huan. Constructing the dual luciferase reporter vector containing human DRD1 promoter region [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6060-6066. |
| [2] | He Yan-ping, Ma De-chun, Li Lei, Zhang Li, Zheng Shuang, Dong Ke-xin. Hemocompatibility and surface modification of artificial blood vessel materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1272-1276. |
| [3] | Ma Fa-ku, Wang Huan, Liu Bin, Yang Yan-li, Su Qin-jun, Qian Zhen, Dong Liang. Expression of CD44+/C-myc+ cancer stem cells and its relationship with the prognosis of patients in colorectal tumors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2161-2166. |
| [4] | Wang Guo-xi, Wang Guo-qian, Zhang Shu-quan. Hyperbaric oxygen combined with Schwann cells transplantation for spinal cord injury in rats: electrophysiological and functional changes of the hind limbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2205-2210. |
| [5] | Liu Lin-lin, Deng Wei-min. Human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene-transfected effects on biological characteristics of Schwann cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2250-2254. |
| [6] | Liang Liang, Xu Tao, Song Yang, Sheng Wei-bin. siRNA lentiviral vectors carrying telomerase reverse transcriptase gene hasten astrocytes apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(11): 1707-1711. |
| [7] | Huang Zhe. Correlation between Bmi-1 and clinicopathological features of colorectal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 894-899. |
| [8] | Li Bing-ting, Jia Ying-zhen, Liu Zhi-fang, Song Yuan, Hou Xiao-wei. Effect of freeze-dried bone xenograft and platelet-rich fibrin compound on osteogenesis and osseointegration of alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8376-8381. |
| [9] | Wu Tao, Wu Jin-hui, Zheng Guo-dong, Lu Zhi-qin, Zeng Hai-yan, Lv Jun, Xing Jian-zhou. Release behavior of icariin-chitosan/hydroxyapatite scaffolds in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8399-8404. |
| [10] | Wang Xiao-dong, Zhang Yong-hong. Preparation and performance of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2-poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyoctanoate) nanospheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8405-8408. |
| [11] | Feng Chao, Li Zhe, Lv Xiang-guo, Xu Yue-min, Fu Qiang. In vitro preparation and biochemical evaluation of oxygen generative keratin/silk fibroin compound biomaterial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8480-8486. |
| [12] | Li Tian-shi, Zeng Wen-ni, He Jun-jun. Chitin and its derivatives inhibit scar formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8504-8508. |
| [13] | Ma Song-feng, Cao Hui, Zheng Feng, Qiao Jun, Zhang Guo-ming. Concomitant cardiac valve replacement and coronary artery bypass grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 699-704. |
| [14] | Ren Cai-ling, Qi Jie, Zhang Jun. Aerobic exercise affects c-Src mRNA expression and c-Src activity in aortic vascular endothelial cells of spontaneous hypertensive rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(49): 7943-7947. |
| [15] | Yu Li-chong, Qian Ye-yong, Shi Bing-yi, Fan Yu, Liu Lu-peng, Yu Fei. Genomics and gene polymorphism of immunosuppressive drugs after kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(46): 7509-7514. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||